Hull House
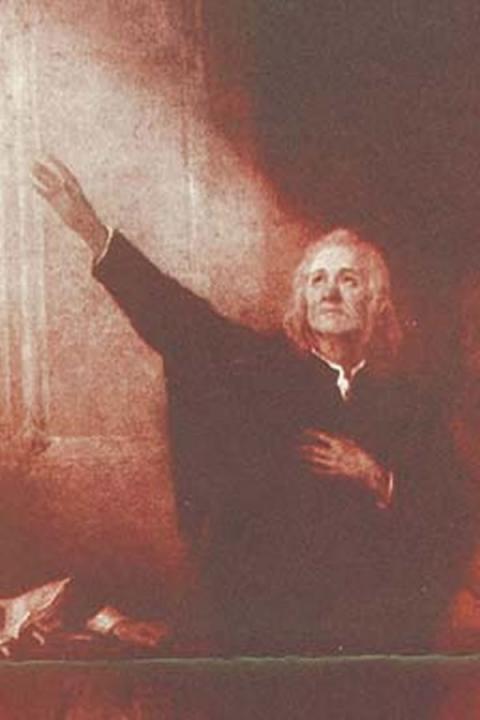
May 17, 2017Jane Addams was raised in a comfortably well-off family in a farming community. So when, as a child, she first saw that some people in the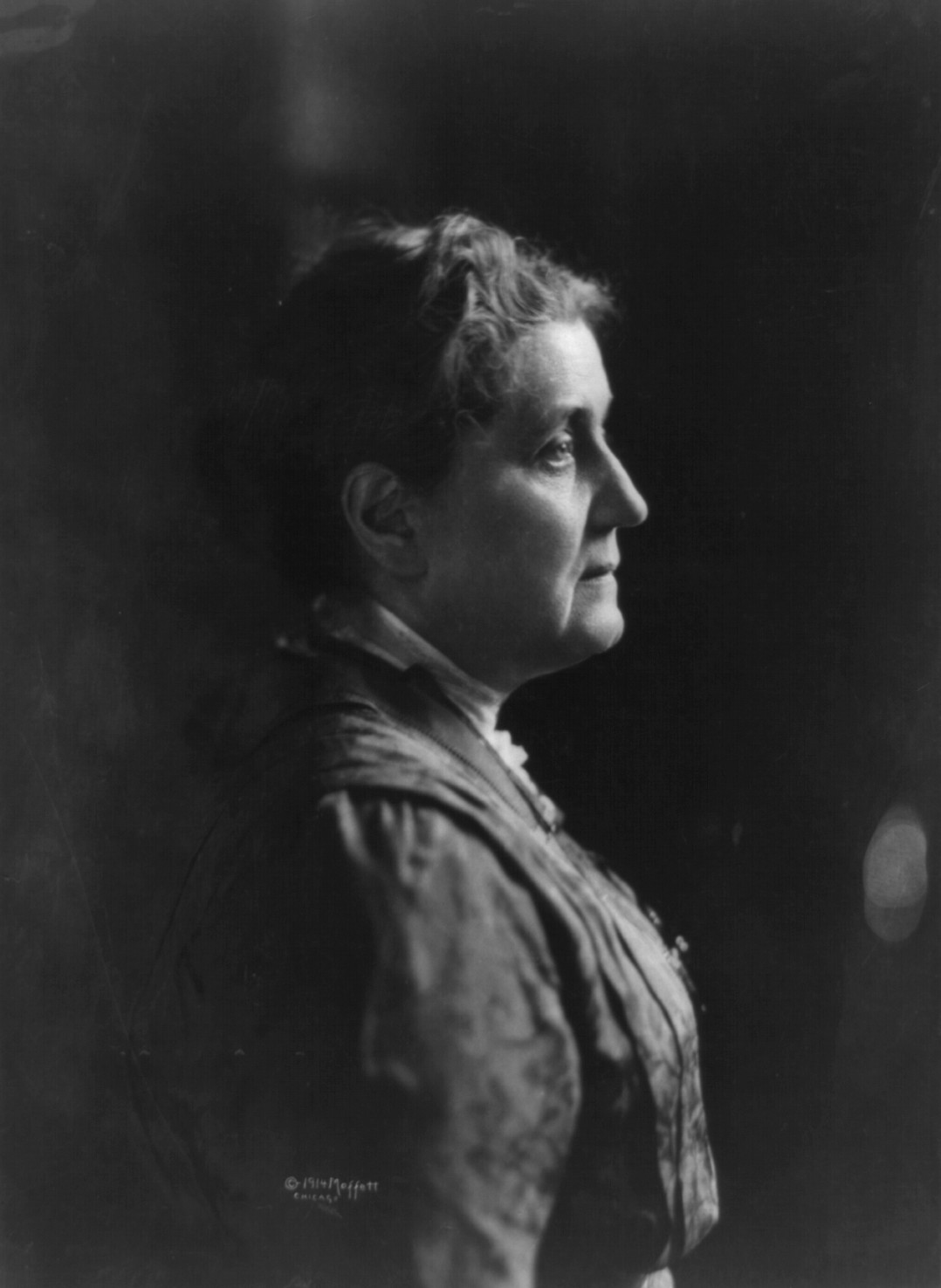  city lived in horrible conditions she was shocked. But instead of wanting to run away, she decided that she wanted to live among those poor people.
city lived in horrible conditions she was shocked. But instead of wanting to run away, she decided that she wanted to live among those poor people.
She grew up to do more than that. In 1889 Jane Addams and her partner Ellen Starr found a big house in an area of Chicago where many recent immigrants lived, often in dirty, crowded conditions of extreme poverty. That house became Hull House, which not only provided a place for 25 women (including Addams and Starr) to live, it also served as a location for people to join clubs, discussions, and activities, as well as take English and citizenship classes, and theater, music, and art classes.
Hull House provided a kindergarten and day care for the children of working mothers, an employment bureau, an art gallery, a museum, and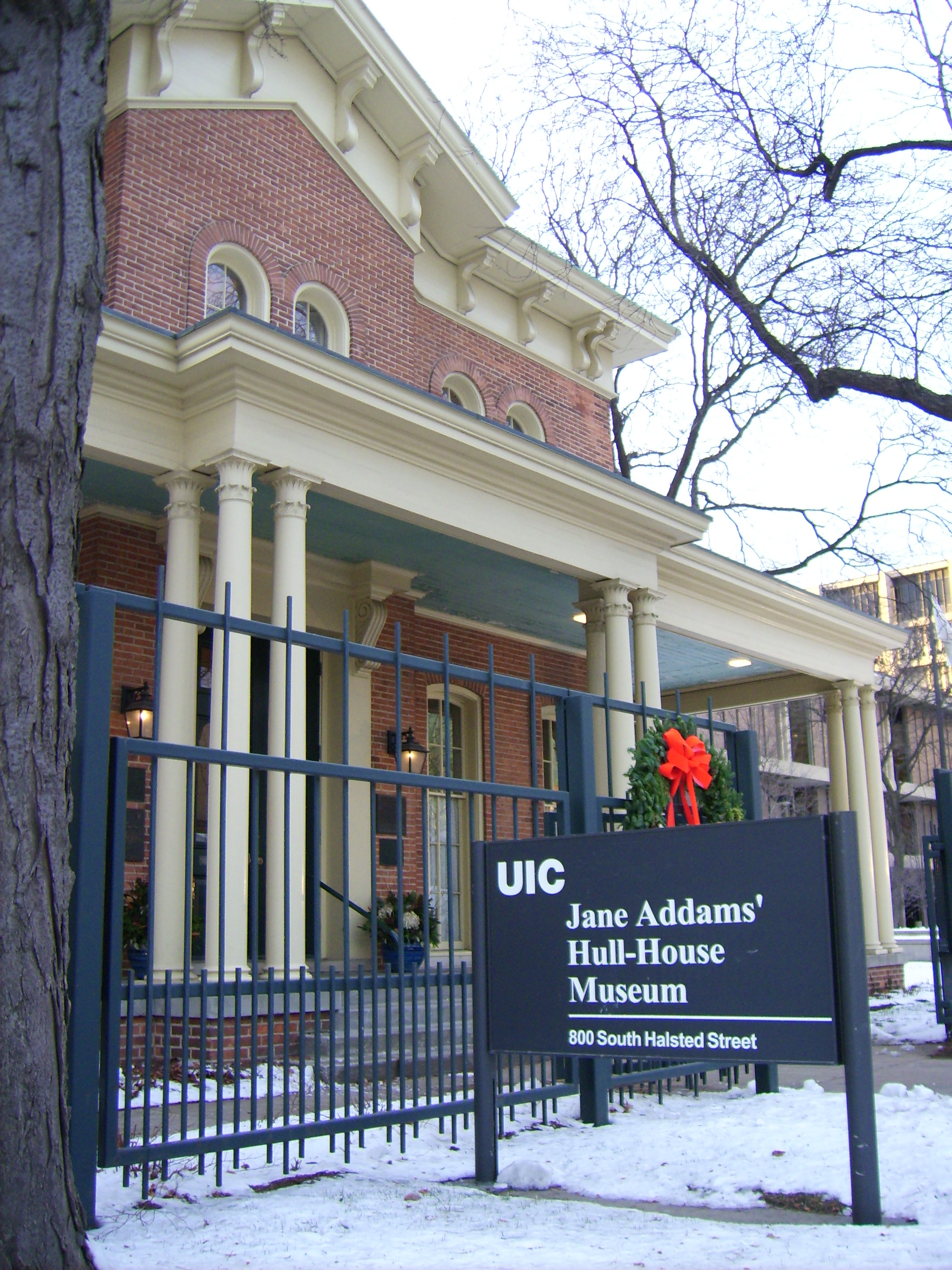  libraries. Those lectures and discussions and classes were places for poor immigrants and wealthier Chicago residents to come together and learn from one another, because Addams strongly believed that people of different social classes had a great deal to teach one another, and that we all are better off when people come together.
libraries. Those lectures and discussions and classes were places for poor immigrants and wealthier Chicago residents to come together and learn from one another, because Addams strongly believed that people of different social classes had a great deal to teach one another, and that we all are better off when people come together.
Learn more by visiting The Jane Addams Hull-House Museum online.
A Creative Life
April 7, 2017Béla Bartók was a Hungarian pianist and composer who added a great deal to our world through his creativity. He started playing piano as a tiny child, and knew 40 songs by the time he was four—and gave his first public recital , including an original composition he’d written two year earlier, when he was eleven.
Bartók went on to become a famous composer who not only wrote his own music, but also went out around the countryside gathering folk music, which he often worked into his compositions. While he was collecting music from the Székely people in Transylvania he learned about Unitarianism.
He liked the idea of a creative religion that was less about following rules and more about connecting with all aspects of life. He eventually joined a Unitarian church in Hungary, and attended with his son.
With the rise of a fascist government in Hungary and the approach of the Second World War, Bartók fled to the United States. He was safe there, but felt lonely and disconnected from his homeland, and it was hard for him to continue to write music. But when he was diagnosed with leukemia and knew that he did not have very long to live, his creative energy returned in a burst and his last compositions are often considered his greatest.
To learn more about Bartók and listen to some of his music, visit the NPR story, “Béla Bartók: Finding a Voice Through Folk Music”
Music: Béla – Evening in the village
Here is one of Bartók’s compositions, titled “Evening in the Village.” The tune comes from a folksong, which is called the “ancient Székely anthem.” The pictures in the video were almost all taken in Transylvania, where Bartók discovered Unitarianism. (The one with the gate was taken in Máriabesnyő, a famous shrine in the outskirts of Budapest.)
All Bodies Need Care
February 2, 2017Clara Barton learned in the Universalist church she was raised in that God is love, and that all lives are precious. As she grew up she took those lessons seriously, recognizing that we are called to care for people’s bodies, not just their souls.
Clara Barton became a teacher, but when the Civil War broke out she was horrified to learn that food and medical supplies weren’t getting to the soldiers, and that many suffered and even died for lack of food, water, and treatment for their injuries.
Although people at the time didn’t think women were strong enough to handle being in the midst of war, Clara raised money for supplies, and snuck in at midnight to a battlefield in Virginia, where she set about cooking food and treating the injured. She even learned how to remove a bullet from a person using just a pen knife!
Clara Barton cared for soldiers from both sides at 14 battle sites. And when the war was over, she was the person who founded the American Red Cross, bringing to the United States the idea of an organization that would care for all people in a crisis, restoring safety and health to bodies.
A New Freedom of Faith
January 3, 2017Throughout the history of Christianity there have been big fights over changes in religious belief and practice, with different people say their version is the real version.
But King John Sigismund, the one and only Unitarian king in history, had a different point of view. Way back in 1561, John Sigismund was very interested in religion, partly because people in his country of Transylvania kept fighting about it. The Roman Catholics, Lutherans, Calvinists, and Unitarians all argued about whose views about God and Jesus and how church services should be conducted were right.
Finally, King John called the best speaker from each church to come to a place called Torda for a debate to decide who was right. The speaker from the Unitarian church was a man named Francis David. He argued that no one has the right to force people to believe anything about God, and that it’s OK if our understanding of religion changes.
After 10 days, King John ordered the debate to end. But he did not announce a winner; he did not say that any of the four churches was the best. Instead, King John agreed with Francis David, and he created what was called the Edict of Torda, which declared that every church and every person would be free to follow their own beliefs, even if those beliefs changed over time. There are still Unitarians in Transylvania today who share that commitment to freedom of belief.
Read more about Francis David from the UUA’s Tapestry of Faith programming, or read the Edict of Torda for yourself!
The Father of Christmas
November 30, 2016This month we celebrate Charles Dickens, British Unitarian, and author of A Christmas Carol. When Dickens wrote A Christmas Carol in 1843, many Christmas traditions had almost died out, and the holiday was hardly celebrated. England was becoming more and more industrial, and people leaving farms to work in factories had left their old customs behind.
But the story, which was wildly popular, brought enthusiasm back to the cities for practices like singing Christmas carols and feasting on special foods. The picture of the Cratchit family celebrating their Christmas together inspired people to find a way to celebrate Christmas in the cities, and the change of heart which comes to Ebeneezer Scrooge reminded people that Christmas was traditionally a time when the wealthy folk shared with the poorer people.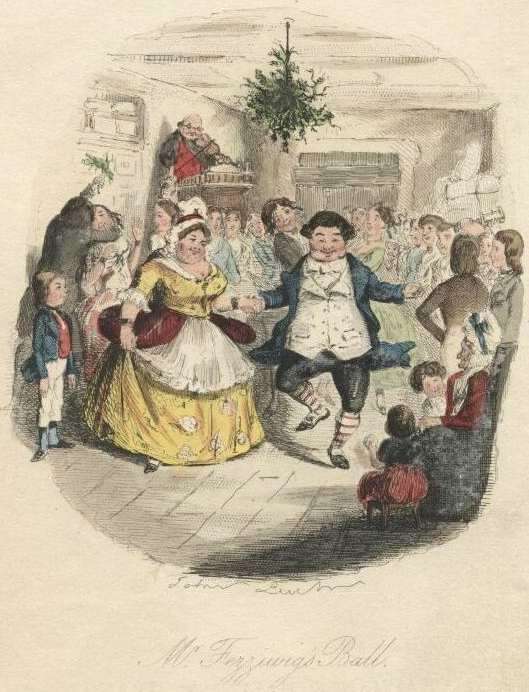
In fact, Dickens was very concerned with the conditions of poor people in England at a time when the gap between the rich and the poor was getting wider and wider. Many of his books deal with this theme, and he became a Unitarian because, as he said, they “would do something for human improvement if they could; and practice charity and toleration.”
Interested in learning more about Charles Dickens, our religious ancestor? Here are a few additional resources:
A 2005 UU World article, “Ebenezer Scrooge’s Conversion,” by Michael Timko, describes how Charles Dickens’s story, A Christmas Carol, exemplified 19th-century Unitarianism.
In the Tapestry of Faith children’s religious education curriculum Windows and Mirrors, Session 13 (Images of Injustice) addresses Charles Dickens, his work and his dedication to improving the lives of the poorest English workers and their families. From the introduction to the lesson:
As Unitarian Universalists, we do not turn away from noticing the gaps that separate “haves” from “have nots.” To work against inequity, we know we first have to see it. Unitarian Charles Dickens saw it. Born poor, he later earned a living as a writer and joined a more comfortable economic class. Dickens used colorful character portraits and complex, often humorous plots, to expose tragic inequities in 19th-century British society. He showed that people at opposite ends of an economic spectrum belong to the same “we,” united by our common humanity and destiny—a lesson which resounds with our contemporary Unitarian Universalist Principles.
The website Charles Dickens online has well as the Dictionary of Unitarian and Universalist Biography offer biographical information and many other resources.
Choosing When to Pray
November 1, 2016Prayer is an important part of the spiritual lives of many UUs—but we also are clear that people need to choose for themselves how and when they will pray. It isn’t the government’s place to decide that for people.
In the early 1960s the UU Schempp family helped to make that clear in American law. Sixteen-year-old Ellery Schempp wasn’t comfortable with having to say the Lord’s Prayer and listen to Bible readings at his public school. His parents, Ed and Sidney Schempp, talked about the issue with Ellery and his siblings Roger and Donna. Together they decided that not only was it not right for Ellery to have to say a prayer he didn’t believe in, no kid should be required to say a prayer that didn’t match their beliefs or faith tradition.
So the Schempps challenged the school in court, and their case went to the Supreme Court. In 1963 the court ruled in Abington Township School District v. Schempp that it was unconstitutional for a public school to expect students to participate in school-sponsored religious activity. The 1st Amendment of the US Constitution guarantees freedom of religion, and a UU family stood up to make sure that children were included in that guarantee.
In the Circle of Love
October 4, 2016The poet Edwin Markham, who was born in 1852, and became the poet laureate of Oregon from 1923-1931, was invited to read his poem “Lincoln, Man of the People” at the dedication of the Lincoln Memorial in 1922.
But UUs most often remember him for a tiny little poem that expresses his Universalist beliefs in love that is big enough to include everyone—and offers a radical understanding of belonging. The poem, called “Outwitted,” says:
He drew a circle that shut me out—
Heretic, rebel, a thing to flout.
But Love and I had the wit to win:
We drew a circle that took him in!
 Think about what the poem says: He wanted to shut me out and say that I didn’t belong. He said that my beliefs made me someone who had to be pushed away. But because I live from a place of love, I did something very clever and sneaky—I found a way to include and welcome him, even when he wasn’t willing to include or welcome me.
Think about what the poem says: He wanted to shut me out and say that I didn’t belong. He said that my beliefs made me someone who had to be pushed away. But because I live from a place of love, I did something very clever and sneaky—I found a way to include and welcome him, even when he wasn’t willing to include or welcome me.
That’s Universalism—love big enough to offer belonging to every human soul. Not because everyone is like us or even necessarily likeable, but because Love is big enough to include everyone.
When did Unitarians begin?
September 1, 2016There are different ways that you could define the beginning of Unitarianism. But many people would say that Unitarians were first defined as a distinct religious movement by William Ellery Channing, in a sermon given in 1819.
In this sermon, called “Unitarian Christianity” (or sometimes “The Baltimore Sermon,” because he gave it at an ordination in Baltimore), Channing laid out what he though were the particular beliefs of the group of liberal Christians who were sometimes referred to as “Unitarians.”
Unitarians, he said, did not believe in the trinity of God the Father, God the Son (Christ) and the Holy Ghost—which is what gave the group the name Unitarian, for the unity of God. But more than that, he described Unitarians as believing in human goodness, and believing in the importance of using reason in looking at religion.
Channing said that thinking is one of the most important gifts that we are given as human beings, and that surely God expected us to to use our gifts of reason in understanding religion as well as the rest of life.
In 1825, just six years later, the American Unitarian Association became the official organization of the Unitarians.
Send in the Clowns
July 6, 2016Most of us only see clowns in parades and circuses. But for refugees and people who cannot go back to their homes, there are not many parades or circuses, and the children who live in the refugee communities don’t get to see many clowns-or have a lot of fun in general. It’s a hard life for anyone, especially for children, but these clowns are clowning for a cause!
Clowns without Borders is a troupe of performers who visit refugee camps and displaced communities and perform for them. They juggle, they do magic tricks, they make everyone laugh and smile. For more than 20 years, these joyful folks have brought joy to the loves of people who have experienced great struggles and loss. They call it Resilience Through Laughter.
Why is this posted in the UU & You section of Family Quest? Because there are UUs participating in Clown Without Borders today! Here’s an interview with lifelong Unitarian Universalist Sarah Foster:
Sarah Liane Foster, a lifelong Unitarian Universalist, traveled as a professional clown with Clowns Without Borders to Haiti, Turkey, Colombia, Swaziland, and South Africa where children have experienced conflict and injustice. “Laughter is a critical way to heal trauma,” Sarah said. You can read more about Sarah’s story in the Spring 2016 Family pages of UU World as well!
A Tale of Two Ministers
June 1, 2016For our theme of Mystery we actually have two people to honor. The first is Rev. Dr. Judith Campbell, a UU minister who writes mystery novels about a UU minister named Olympia Brown. The second, of course, is the original Rev. Olympia Brown, who the character is named for.
The Olympia Brown in the murder mysteries is, like her author, a modern woman. But she shares a courageous spirit and a sense of justice with the historical Olympia Brown.
That Olympia Brown was born in 1835, and she was the first woman in the U.S. to graduate from a regular school for the ministry, and she was ordained into the Universalist ministry as the first woman to be fully ordained and recognized by her denomination.
Olympia Brown served as a minister until the age of 53, when she decided to retire from church work in order to work full time on promoting women’s rights.
Judith Campbell, our mystery writer, has been both a professor and a minister before turning to writing murder mysteries as well as other kinds of literature.
Renew Your Membership
We invite you to join your fellow CLFers to renew your CLF membership and stewardship of the CLF for another year.
Support the CLF
Can you give $5 or more to sustain the ministries of the Church of the Larger Fellowship?
Newsletter Signup
About
Quest for Meaning is a program of the Church of the Larger Fellowship (CLF).
As a Unitarian Universalist congregation with no geographical boundary, the CLF creates global spiritual community, rooted in profound love, which cultivates wonder, imagination, and the courage to act.
Contact
Church of the Larger Fellowship Unitarian Universalist (CLFUU)
24 Farnsworth Street
Boston MA 02210







