Making Justice Now
May 2, 2016Usually we honor someone from our history who serves as a role model on this page, but there are plenty of UU justice-makers who are living and working right now.
Take, for instance, Lena K. Gardner, who is the Membership and Fundraising Director for our own Church of the Larger Fellowship. Lena is a leader with the Black Lives Matter movement in Minneapolis, Minnesota. She organizes and speaks out and brings people together to protest racist ways that the police have treated Black people in their community and other places around the country.
Working with many other people—many of them young adults or even teenagers, they have protested police killing unarmed Black people and demanded that city officials change policies to hold police accountable.
Always using peaceful strategies, they have held protests in America’s biggest shopping mall and on the highway and in front of a police station.
Some people have objected to the Black Lives Matter slogan, saying that all lives matter. But Lena and many others are pushing people to understand the many ways in which Black people are treated as if their lives don’t matter. They are working for a world where everyone finds fairness.
Moving Toward Freedom
March 31, 2016Frances Ellen Watkins Harper was born a free Black woman in Baltimore, Maryland in 1825. She was raised in the household of her uncle, an educator and African Methodist Episcopal (AME) minister. He was also an abolitionist—a person who objected to the enslavement of blacks. Harper became an educator and abolitionist as well. She also became a writer, publishing her first book of poetry at twenty and later in life publishing the first short story by an African American woman. Her writing often urged Blacks, women, and people in oppressed groups to take a firm stand for equality and freedom.
In 1850, the Fugitive Slave Act was passed. It became dangerous to be a free Black in Maryland because slave owners could claim Black people were runaway slaves and force them into slavery. So, Harper moved farther north to Ohio and then to Philadelphia. She taught, ran part of the Underground Railroad helping slaves escape to freedom, and lectured around the country.
In 1863, abolitionists celebrated success with the passage of the Emancipation Proclamation, which freed the slaves. But there was a long road ahead to full equality, and Harper spent the rest of her life working for women as well as African Americans to have access to full freedom and justice.
To read some of Harper’s poems click here.
Whole, Not Broken
March 1, 2016Christopher Reeve had everything going for him. He was handsome and athletic and famous for playing Superman in the movies. He had a lovely family and plenty of money that he’d made as a movie star. Really, things could hardly have been better.
Until he was in a horse bock riding accident that damaged his spine and left him paralyzed below his neck. He couldn’t move his hands or feet, let alone play a superhero who could jump tall buildings in a single bound. He was, in a profound way, broken.
But in many other ways, he was deeply whole. He had a family who loved him and believed in him. And he found in his Unitarian Universalism a reminder that one way we can build wholeness for ourselves is by doing what we can to build wholeness for others.
So Christopher and his wife Dana dedicated themselves to trying to make life better for other people who had spinal cord injuries. They raised money to help people get things they needed like ramps and vans that could carry wheelchairs. And they raised money for research that might help people with spinal cord injuries.
Christopher Reeve eventually died from the complications of living with his injury, but his living taught a lot of people about what can be whole when things get broken.
A House for All
February 1, 2016You could argue whether Jane Addams was a Unitarian, since she regularly went to a Unitarian church, but never joined. But you can’t argue about whether she understood the true meaning of hospitality.
Jane grew up in a wealthy family, but when she discovered as a child that many poor people in the cities lived in terrible conditions, she wanted to make a difference. In 1889 she and Ellen Starr founded Hull House, a big house in Chicago which offered a place for the many poor recent immigrants in the city to take part in clubs, discussions, and activities, as we ll as take English and citizenship classes, and enjoy theater, music, and art classes.
About 25 people actually lived at Hull House, and Jane made sure that both wealthier people and poor immigrants lived there together, since she believed that people with different experiences could learn a lot from each other. Jane Addams and the other women who ran Hull House with her created an amazing space of hospitality where people could learn, grow and have fun together. In 1931 she was awarded the Nobel Peace Prize.
Learning More Online:
To learn more about Hull House, and the visionary women who founded it, visit the National Women’s History Museum website. The Jane Addams-Hull House Museum today serves as a living legacy to Jane Addams and her vision of hospitality for all; learn more about their ongoing work at hullhousemuseum.org
An Unexpected Second Chance
January 1, 2016John Murray was a Universalist who certainly took starting fresh to heart. Tragedy struck for Murray when his wife and young son died, and then he was put in jail because he was unable to pay his bills.
In 1770 he felt able to make a totally fresh start, so he got on a ship and headed for the New World, North America. Unfortunately, the ship got stuck just off the shore of New Jersey, when they were trying to get to New York.
But Murray agreed to go on shore and try to find directions and supplies. He ended up on the doorstep of a man named Thomas Potter, who greeted him as the Universalist preacher that Potter had been waiting for!
Well, Murray didn’t have plans to be a Universalist preacher—that wasn’t the fresh start he had in mind. He wanted to go on to New York. But he agreed that if they didn’t get the wind the boat needed to sail on, that he would preach on Sunday about Universalism’s message of an absolutely loving God.
Well the wind didn’t pick up, and Murray did preach, and he ended up making a fresh start by marrying Potter’s daughter and becoming a traveling preacher, spreading the good news of God’s love all over New England.
A Legacy of Hope
December 1, 2015Why, you might ask, would we honor James Lord Pierpont? James, who was born in 1822, grew up a Unitarian, but it was his father John who was the minister. John was also an abolitionist, someone who fought against slavery. But James actually fought on the side of the South during the Civil War.
James married and had children, but he left them behind to start a business as part of the California Gold Rush. His business failed after his goods burned up in a fire. A few years later his wife died, and James left his kids with his father as he followed his brother Rev. John Pierpont, Jr. to Savannah, Georgia, where the younger John Pierpont was called to serve a Unitarian church.
So what about this makes James Pierpont so special? Nothing. It was a lot of failure and sadness. Except that somewhere around the time that he moved to Savannah, James wrote a little song you might have heard. He called it “The One Horse Open Sleigh,” but you might know it as “Jingle Bells.”
When he was going through trouble and loss, James Pierpont could have no idea that he would create something that 150 years later would be part of the joyful holiday season for millions of children and adults. That’s hope for you.
The Longest Journey
November 2, 2015Many Unitarian Universalists have gone on long and meaningful journeys, but none has gone quite as far as Clyde Tombaugh.
Clyde was born 1906, and ever since he was little he wanted to be an astronomer. A hailstorm that destroyed the family’s crop meant that there was no money to send him to college, but he built telescopes and lenses on his own.

The astronomer Clyde Tombaugh, discoverer of Pluto here shown with his homemade 9-inch telescope. Photo circa 1930, Public Domain
People at the famous Lowell Observatory were so impressed with his drawings of Jupiter and Mars that they offered him a job.
While he was working at the Lowell Observatory Clyde Tombaugh explored the sky using photographs taken through a telescope, and through a special procedure discovered that what he suspected was true—there was another planet out beyond Neptune.
Although that planet, Pluto, was later reclassified as a dwarf planet, it was an important discovery about our solar system.
What about the longest journey? Well, Clyde Tombaugh died in 1997, at the age of 90. He was cremated, and some of his ashes went onto the New Horizons spacecraft that made it all the way to Pluto, and recently sent us back stunning pictures of the dwarf planet at the edge of our solar system.
Truly an amazing journey!
In Search of Abundance: Margaret Fuller
October 1, 2015Margaret Fuller, born in 1810, believed that women should lead full and abundant lives, even though most people at the time thought that being a wife and a mother was quite enough for women to do.
But Margaret was not only extremely smart, she liked to be in conversation with other people, exploring ideas and thinking about how the world could be better. She was good friends with famous intellectuals of the time, like Emerson and Thoreau. But she especially liked to make a place for women to have conversations that would be a chance for “self-expression and independent thinking.” Many women who participated in these conversations went on to be leaders in the movement for women’s equality.
In 1846, the quest for more abundant life took Margaret Fuller to Europe, where she worked as a foreign correspondent, sending newspaper articles about events in Europe back to the United States.
While in Italy, Margaret became involved in the Italian revolution, and fell in love with another revolutionary, a younger man who was an Italian noble. The two of them had a son, and eventually decided to come back to the US. Sadly, their ship sank in a storm within sight of shore, and they never made it back. But while she lived, Margaret Fuller certainly lived abundantly!
To learn more, visit margaretfuller.org.
“A house is no home unless it contains food and fire for the mind as well as the body” -Margaret Fuller
Adin Ballou: Peace and Forgiveness
August 31, 2015This month, as we think about forgiveness, we honor Universalist minister Adin Ballou (not to be confused with his earlier Universalist ancestor Hosea Ballou).
Adin Ballou came to believe that his religion called him to practice peace in all things, following the message of Jesus, who said that if someone slaps your cheek, that rather than hitting back it is better to offer your other cheek to be slapped.
Adin founded a community called Hopedale, which was based on these principles of radical peace and non-violence.
One day a man came to Hopedale, hungry and homeless. They offered him food and a place to stay the night. Later that night two young girls heard noises downstairs and went to investigate. They saw feet sticking out from the couch, and a bag full of dishes and candlesticks!
They called their parents down, and quickly determined that the feet belonged to the man they had fed and sheltered. The parents called in their community leader, Adin Ballou, who helped the man out from under the couch. The man explained that he was desperate, with no food or job, and he figured that if he was caught stealing he would be sent to jail, where at least he would be able to eat. Instead of sending the man to jail, Adin not only forgave the man, he even invited the him to join their community, and to make a home with them!
The Stargazer Who Discovered a Comet
July 1, 2015From “The Stargazer Who Discovered a Comet” in The UU Kids Book by Anne Fields and Charlene Brotman (Biddeford, Maine: Brotman-Marshfield, 1989); used with permission. “Afterward” from Rooftop Astronomer: A Story about Maria Mitchell by Stephanie Sammarti
NOTE: The name, Maria, is pronounced “ma-RYE-ah.”
Maria always remembered the day she helped her father time an eclipse of the sun. She used the chronometer to count down to the exact second that the moon began to block out the sun. Her father needed to send the timing report to his astronomer friends at the big Harvard University observatory, where they were collecting eclipse information from all over.
“There will be another eclipse like this in 54 years,” said father.
“I’m twelve now, I’ll be 66 then!” exclaimed Maria. How could astronomers know so far ahead what would happen in the sky? How amazing that the stars and planets spun around in such order!
“I want to study the stars, always!” decided Maria one day. “I want to be an astronomer!”
“Father, can only men be astronomers?” she asked.
Father thought for a moment, while Maria watched his face anxiously. He knew that no matter how smart a girl was, she could not get into any college in the United States to study astronomy. Only boys were allowed to go to college in those days.
Finally he said, “There are no women astronomers in America. There are only a few in the entire world, but I do think it’s possible, Maria. I will teach thee all I know about astronomy. Cousin Walter has scientific books he might let thee read. Thee will need to study mathematics. That is as important to astronomy as the telescope. Yes, I do think it is possible thee could be an astronomer.”
“Oh, I will study, father, I will!” cried Maria joyfully, hugging her father.
True to her word, Maria spent long hours studying geometry and trigonometry in a tiny room at the foot of the attic stairs . . .
Maria still spent most evenings studying the sky with the telescope and keeping careful records on the stars. One night she saw a fuzzy spot through the telescope that she had never seen before. Quickly she checked the charts to see if a star was supposed to be in that place in the sky. No star was ever there. Could it be a new comet?
“Father, come up and look quick!” she shouted. Her father dashed up the attic stairs to the roof and peered carefully through the telescope.
“Thee’s discovered a comet above the North Star!” he exclaimed. “We must write immediately to the Harvard Observatory and tell them! A comet is named for the person who discovers it first but the discovery doesn’t count unless it is reported to an observatory.”
They wrote the letter that very night, but to their dismay, a storm at sea delayed the mail in leaving the island for two days. Soon the comet was also sighted by someone in Italy, then in England and in Germany. The King of Denmark had promised a gold medal to the first person who discovered a comet that could be seen only through a telescope. Would Maria miss getting the medal because her report was late? Months went by while this was being decided!Finally one day a package arrived for Maria from the King of Denmark. It was the gold medal! Now Maria was famous. She was the first woman in the world to have a comet named after her!
Women all over America were so proud of Maria that they collected money for a new, larger telescope for her. How excited she was! Now she could learn so much more about the stars and planets!
Maria’s life changed in 1865 when a wealthy man named Matthew Vassar had the courage to start a college for women — Vassar College in Poughkeepsie, New York.
People called Matthew Vassar an old fool. They said girls didn’t need a college education, they just needed to know how to sew and do housework and maybe play the piano a little. College would ruin them for doing housework.
There were ministers who thundered, “It’s against the will of God for girls to go to college! It will break up families and destroy the country!”
In spite of such talk, Matthew Vassar wanted Maria to come and teach astronomy! She could have an observatory with the third largest telescope on the continent.
“Father, how can I do this?” said Maria softly, trying to keep her voice from trembling. “I’ve never even been to college myself!” She was also thinking, “If I’m not any good at it, then people will say, “This proves that women have no business teaching in colleges!”
“Thee can do it, and do it well,” said her father. “Thee should have no fears.”
He was right. Maria’s students loved her. The other professors just expected the students to sit and listen to them talk, but Maria taught her students to question everything and experiment, and to think for themselves.
Afterward
In 1986 another young woman discovered a comet. Working at Mount Palomar Observatory near San Diego, California, Christine Wilson had equipment and techniques at her disposal undreamed of in Maria’s time. At the start of her career, she had a knowledge of astronomy surpassing all that Maria learned in a lifetime of study.
But Christine Wilson’s discovery, while exciting and well publicized, did not catapult her into sudden fame as Maria’s had. New comets are not headline news. Thanks to pioneers like Maria, neither are women astronomers. Women now occupy important positions in the scientific community. Side by side with their male colleagues, they fight disease, predict the weather, design computers, and continue to discover comets. Maria Mitchell would be pleased.
From Session 2 of the Toolbox of Faith Curriculum, part of the Tapestry of Faith Curriculum offerings from the UUA. Find the complete curriculum here.
Renew Your Membership
We invite you to join your fellow CLFers to renew your CLF membership and stewardship of the CLF for another year.
Support the CLF
Can you give $5 or more to sustain the ministries of the Church of the Larger Fellowship?
If preferred, you can text amount to give to 84-321
Newsletter Signup
About
Quest for Meaning is a program of the Church of the Larger Fellowship (CLF).
As a Unitarian Universalist congregation with no geographical boundary, the CLF creates global spiritual community, rooted in profound love, which cultivates wonder, imagination, and the courage to act.
Contact
Church of the Larger Fellowship Unitarian Universalist (CLFUU)
24 Farnsworth Street
Boston MA 02210


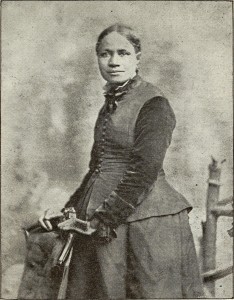



![By H. Dassell [Public domain], via Wikimedia Commons](https://www.questformeaning.org/wp3/wp-content/uploads/2015/07/Maria_Mitchell-253x300.jpg)

